Course Introduction
在交大材料系學生能含跨learning about the structure, properties, and interactions of materials. The field of materials engineering is quite broad. Industries such as information technology, communications, electromechanics, energy, chemical materials, defense, and daily life all rely on the foundation of materials science. Furthermore, the production and manufacturing of any product requires materials. Many bottlenecks in the creation of key components across various fields can only be resolved through the development of new materials or the improvement of material processing. As such, materials engineering professionals are in high demand in the industry, and thus, the materials engineering field is unlikely to become obsolete.
>交大材料課程特色
- Flexible Course Options
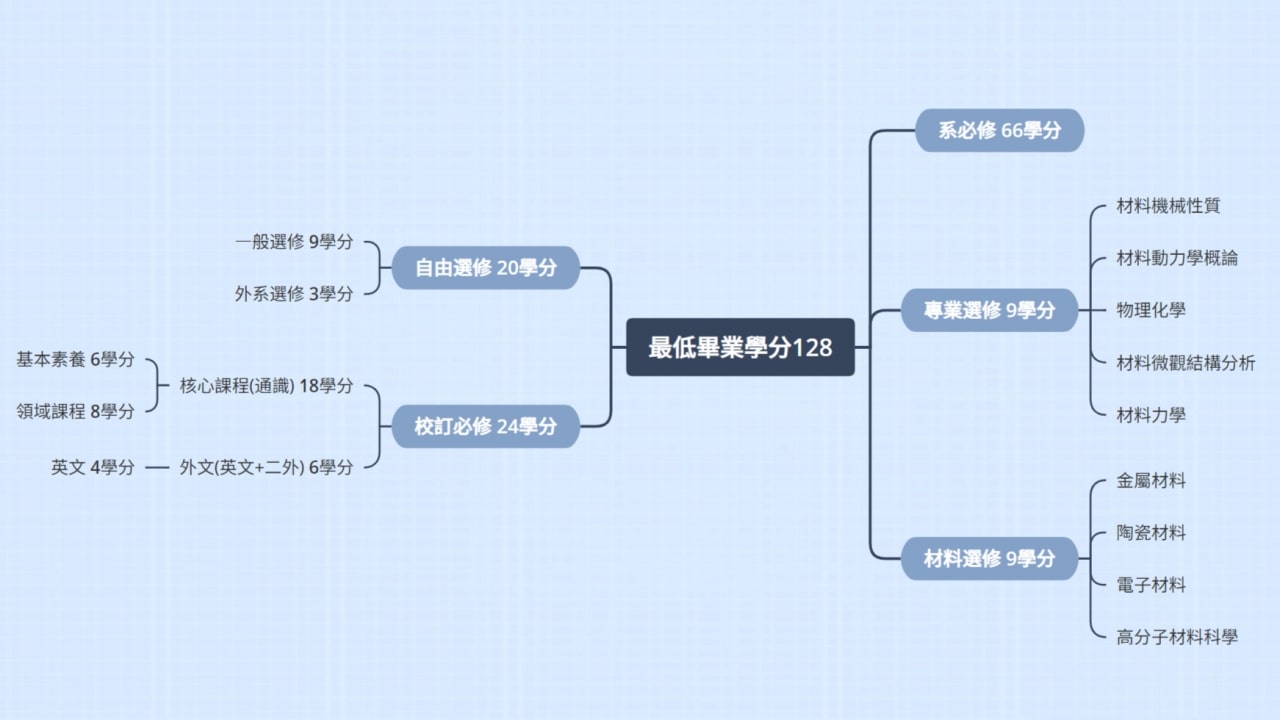
Only 66 credits are required as mandatory courses by the department, providing students with great freedom in course selection. - 三一學程
材料系、光電系、電物系合作的跨領域學程,設計給尚未確定興趣的學生,可探索工學院、電機學院、理學院的各項課程,從中了解自己的興趣和天賦,並培育材料、光電、電子物理的跨領域人才。共有十項模組課程,讓學生依興趣選擇其中三項(或以上)進行修課。修習三一學程的學生,本系必修只需38學分,跨領域的模組課程,彈性運用時間,加強發展第二專長。1. 電物
電子物理系與材料系的相關合作主要是在半導體方面,電物系擁有的專業量子理論,與材料系的半導體製程相輔相成,可以讓材料系和電物系的學生,了解半導體產業的製程端與理論基礎的關係。2. Optoelectronics
In the study of the properties of light and electricity, the Department of Optoelectronics often requires advanced and superior materials for support. The knowledge learned in the Department of Materials Science can be applied to this field, particularly in the areas of optoelectronic semiconductors and solar panel applications, which are areas where collaboration between the Department of Optoelectronics and the Department of Materials Science is highly beneficial.3. 材料
材料科學與工程學系在三一學程中扮演的角色,是讓學生認識材料結構與性質的關係,以及材料的製造過程;根據不同的研究方向,學生可選擇感興趣的相關課程,並與電物系與光電系的知識相互銜接。
Introduction to the Core Requirements of the Materials Science Department
Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering
- Time: First Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: The theoretical foundations of materials science, covering the basic concepts of materials science and materials engineering. The course content will include atomic structure, material microstructure, mechanical properties, optical and thermal properties, material defects, phase diagrams, strengthening mechanisms, and more. This will lay the groundwork for future studies in materials science, providing essential prerequisite knowledge. The course will also provide an overview of the basic science and applications of ceramic materials, polymer materials, electronic materials, magnetic materials, composite materials, and semiconductors.
- Click here to view OCW
Materials Thermodynamics
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: The first semester focuses on the fundamentals of the three laws of materials thermodynamics. Materials Thermodynamics II will extensively apply the three key thermodynamic concepts learned in Materials Thermodynamics I to unit and multi-phase equilibrium, gas molecular behavior, solution behavior, and more.
- Click here to view OCW
Physical Metallurgy
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: This course covers the basic applications of phase diagrams, diffusion behavior, nucleation and growth, as well as phase transformation behavior. It also discusses various material analysis methods and their applications. Upon completing this course, students will be able to explain fundamental metallurgical phenomena, distinguish the composition and properties of different alloys, and understand the properties of metal structures.
Introduction to Crystal Structures and Diffraction
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 3 credits, only in the second semester
- Course Description: This course primarily covers the following topics: 1. The basic crystallography concepts, including the symmetry, classification, point groups, and space groups of crystal structures, as well as important crystal structures. 2. Introduction to X-ray sources, the construction of reciprocal lattices, the basic principles of X-ray diffraction, and various fundamental applications of X-ray diffraction in materials analysis.
Introduction to Computer Science
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 3 credits, only in the first semester
- Course Description: Programming has become a common skill in the engineering field, and materials science often uses programming to simulate the microscopic structure and properties of materials. This course is therefore a mandatory requirement for the department. In this course, students will have hands-on opportunities to become familiar with Python syntax.
Basic Materials Laboratory
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: Students will apply the theoretical knowledge learned in class to conduct a series of materials experiments, covering areas such as metallography and electrochemistry.
Materials Engineering Laboratory
- Time: Third Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: This is a more advanced laboratory course. In this class, students will learn polymer synthesis, preparation, and characterization, as well as the analysis of the optical and electrical properties of polymers.
>Course Map