ADMISSION / 招生資訊
- 交大材料甲乙組介紹
- University and Department Selection Advice
- Career Opportunities After Graduation
- 傑出研究介紹
- Introduction to Alumni Studying Abroad
- Supplementary Materials Courses for senior high school students
- Course Introduction
- University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 3+2 Dual Degree Program
- 交通大學攜手台積電開設半導體學程
分科測驗交材分為甲乙組,你知道不同在哪嗎?
- Physics (Subject-Specific Test) X1.0
- Chemistry (Subject-Specific Test) X1.0
- Mathematics A (Subject-Specific Test) X1.0
- Natural Science (University Entrance Exam) X1.0
- English (University Entrance Exam) X1.0
►交大材料系甲組—3+2學程與5萬入學獎金等你拿
>雙聯學程 優先推薦<
分科選填甲組的學生,將優先被推薦到美國伊利諾大學香檳分校。(美國材料系排名前五的頂尖大學)
3+2雙聯學程,顧名思義是讓學生可用5年時間獲得交大學士及伊利諾大學碩士學位,比正規的時程提早了一年,可因而早點進到美國業界工作,競爭力大幅提升。美國材料碩士的起薪約240萬台幣 (8萬美金),相對於一般學制,進入此學程就相當於能多一年的工作薪水和年資。(請點#美國伊利諾大學 查看更多資訊喔)

>獎學金制度5萬入學獎學金等你拿<
在分科選填志願時,交大材料系將獨立出3位名額,成為獨立的志願序,給選填交大材料系甲組的同學每人5萬元的入學獎學金,註冊即可發放,學生亦不需另做申請,吸引極為優秀的分科生來交大材料系!(請點#交材指考甲組 查看更多資訊喔)
►交大材料系乙組—在校表現好,一樣可以申請各項資源
>Both Group A and Group B can apply for the TSMC Program.<
>甲乙組皆可申請 跨領域三一學程<
另也有材料系、光電系、電物系跨領域設計之的三一學程,是設計給尚未確定興趣的學生,可探索工學院、電機學院、理學院的各項課程,從中了解自己的興趣和天賦,並培育材料、光電、電子物理的跨領域人才。修習三一學程的學生,本系必修只需38學分,跨領域的模組課程,彈性運用時間,加強發展第二專長。(請點#三一學程 查看更多資訊喔)
另外,乙組學生表現優良且在校成績可圈可點,也可申請3+2雙聯學程喔!
(For any inquiries, please contact the Department of Materials Science Office at NYCU, 03-5712121*55302)
University and Department Selection Advice
Recently, many students and parents have inquired about the career prospects for graduates from different departments, so we would like to provide some clarification. If you are very certain about which field you want to pursue, the job opportunities after graduation should not be a major concern. Once you perform well in your chosen field and become a top talent, I believe you will find a job that you enjoy, regardless of whether the field is popular. We strongly encourage students to choose their departments not only based on their interests but also in alignment with their natural abilities. For example, departments such as Electrical Engineering, Electronics, Information Technology, and Mechanical Engineering require strong skills in mathematics and physics to excel. The Materials Science department requires expertise in physics or chemistry. However, students who enjoy mathematics can also pursue new directions in materials theory and computation.
However, if you are unsure about which department to choose, career prospects become an important factor, as your job after graduation will be something you do for over 40 years and will have a huge impact on your life. According to the current industry landscape and future trends in Taiwan, the semiconductor manufacturing industry remains the best choice in terms of salary, working environment, and future competitiveness. Most students from National Chiao Tung University and National Tsing Hua University, especially those in engineering fields, enter this industry. While graduates from different departments may work in the same type of semiconductor manufacturing companies, the nature of their work and opportunities for promotion may vary. The following analysis is provided for reference, as Taiwan's society needs talent in various fields to promote overall development. We are not trying to diminish other departments but simply answering common questions asked by students and parents. We have compiled this information for your reference. This analysis is based on the current industry in Taiwan, and trends may differ in other countries. For instance, in Indonesia, chemical engineering graduates have better job prospects than materials science graduates due to the country's oil production and lack of chip manufacturing.
Mechanical engineering graduates typically work as equipment engineers in semiconductor manufacturing companies. Their job involves maintaining machinery in clean rooms, usually requiring a shift work schedule, including night shifts. Since these machines are designed to produce specific materials, even in companies that sell semiconductor equipment, such as Applied Materials and Lam Research, graduates with materials expertise are the main workforce. For example, in Taiwan, the presidents of Applied Materials over the past decade have all been graduates of the materials science department. While the robotics and drone industries look promising, Taiwan's industries in these fields lag behind Japan and the U.S. by a significant margin, so opportunities are clearly fewer compared to semiconductor companies.
Graduates with a chemical engineering background typically work in traditional chemical plants (e.g., Chang Chun Petrochemical, LCY Chemical) if not in the semiconductor industry. Within semiconductor manufacturing, they are often responsible for specific stages of the manufacturing process. This is because chemical engineering expertise focuses on transport phenomena and unit operations, with knowledge primarily in fluid and gas system laws for material manufacturing. As a result, chemical engineering graduates are often employed as process engineers, typically handling processes such as electroplating or chemical vapor deposition to create specific materials. In semiconductor manufacturing companies, the most common path for promotion is becoming a process integration engineer, someone who understands every stage of the manufacturing process. Materials science graduates are the main talent for this role, as they study various materials, such as electronics, ceramics, polymers, and metals. This is why many Taiwanese schools have changed the names of their related departments to include "Materials Engineering," and after renaming, their rankings often improve, attracting better students. In recent years at NCTU, many students who have studied related departments for one or two years and performed well in their studies have applied to transfer to the materials science department, as it offers broader career options after graduation.
Graduates of the Department of Computer Science typically work in programming-related roles. The field of computer science evolves rapidly, so graduates often need to learn new programming languages or computational methods to stay up to date. There are indeed many large companies in this field, such as Microsoft, Apple, Facebook, Google, and Yahoo, but Taiwan mostly hosts their branches, and there are fewer opportunities for research and development positions.
Therefore, materials science graduates are the mainstream talent in semiconductor-related high-tech companies, which is why materials science is so popular in Taiwan. Additionally, because we cover a wide range of fields including electronics, ceramics, polymers, metals, biomedicine, and nanomaterials, along with theoretical computation, students can easily find their interests in one of these fields once they enter the department, based on their natural talents in physics, chemistry, or mathematics. Furthermore, materials science provides a solid foundation in subjects such as materials thermodynamics, physical metallurgy, crystal structures and diffraction, materials dynamics, crystal defects, metallic materials, electronic materials, polymer materials, X-ray diffraction, and heat treatment. Since the scope is broad, it requires extensive learning time. As Academician Jing-Ning Du has said, we often hear of young and excellent physicists and mathematicians, but very few young, exceptional materials scientists. This is because materials science students must learn about different materials fields, which takes time. However, from another perspective, these materials knowledge, combined with work experience, will become an important asset in your life. As a result, senior materials engineers play an important role in companies and are less likely to be replaced by younger talent. Moreover, materials engineers do not have to spend long hours in clean rooms. The operation of cleanroom machinery is carried out by on-site operators (usually requiring only a high school education). Materials engineers, who typically hold master's or doctoral degrees, are responsible for planning experiments, analyzing results, identifying problems, and implementing improvements—tasks that require critical thinking.
The above analysis is based on the current industry landscape in Taiwan, and different countries may have different trends. If you plan to study in the United States and stay there after graduation, computer science generally offers better job opportunities and slightly higher salaries than materials science, as major companies in this field are based in the U.S. However, materials science graduates, if they are in the right field, can also find excellent and well-paying jobs in the U.S. For example, most UCLA materials science Ph.D. graduates from Academician Du Jing-Ning's lab are working at Intel, and one is at Apple. In recent years, starting salaries for new graduates have exceeded 3.5 million NTD. This is for your reference.
We look forward to having outstanding students like you join us, and we wish you success in your academic journey, wherever you decide to study.
Career Opportunities After Graduation
In the high-tech industry, the materials field plays a crucial role in technological breakthroughs. The students nurtured by the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University are highly sought-after talents by major companies, and upon graduation, they can become industry engineers. In addition to becoming engineers, graduates of the materials science department also have various career paths available, such as becoming academic researchers or pursuing further studies abroad—both are options that offer the potential for success and achievement.

>The Role of Materials in the High-Tech Industry
Materials are present in various industries, such as the LED industry, solar energy industry, microelectronics packaging industry, and semiconductor industry. Taking the example of smartphone manufacturing, a smartphone incorporates the integration of heterogeneous materials, including semiconductors, metals, ceramics, and polymer materials.
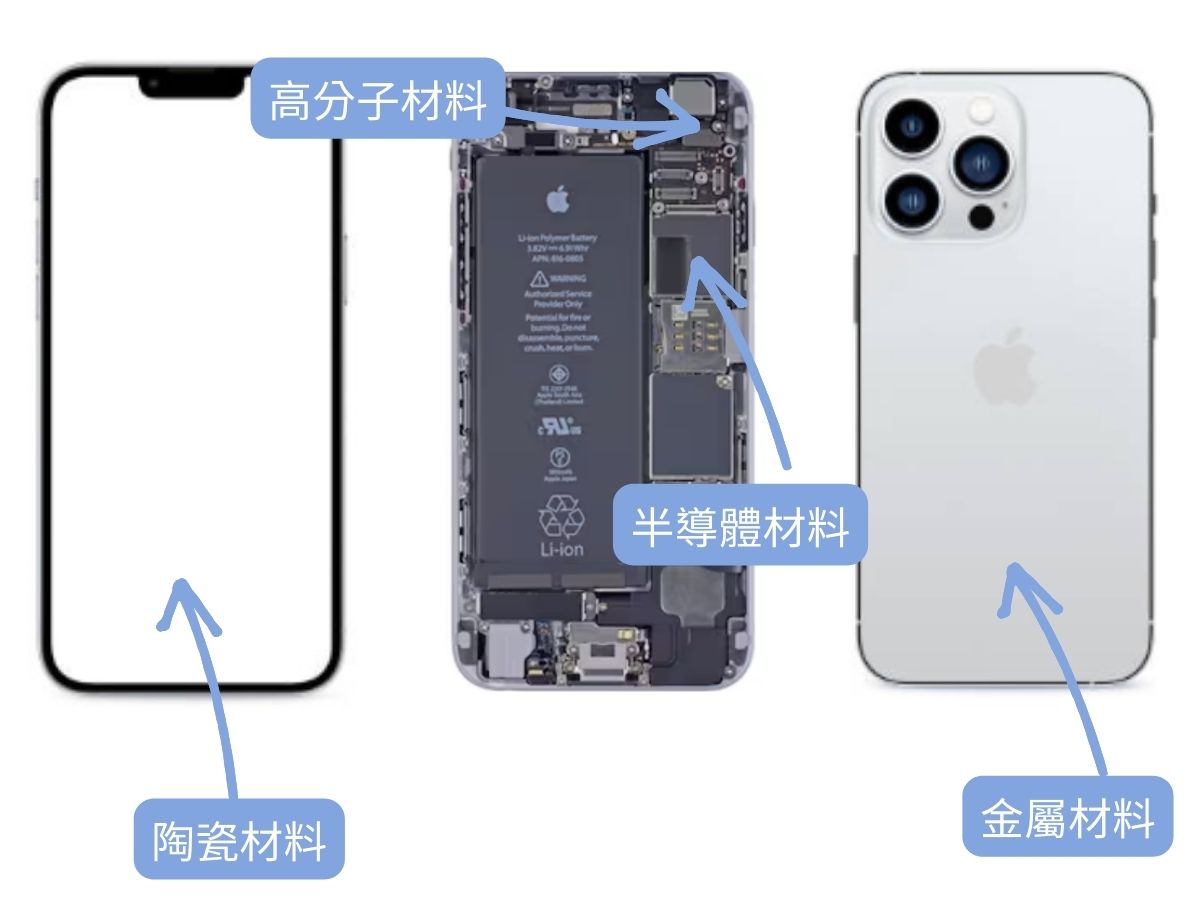
>There are various career paths after graduation.
Additionally, one of the future options for graduates is to engage in academic research at national academic institutions such as ITRI (Industrial Technology Research Institute) or Academia Sinica.

>交大培育高科技人才
According to a report by *CommonWealth Magazine*, 63.5% of the chairman and general manager-level positions in the Hsinchu Science Park are held by alumni of National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University. Additionally, about 80% of the publicly listed companies in Silicon Valley founded by Chinese entrepreneurs are led by alumni from the university.
另外,交大有著全國最領先的科技研發,也培育出許多科技業佼佼者。交大材料的學生大部分畢業後會就讀研究所,而出社會則進入台積電,若有就讀博士,進入台積電的起薪會較高。
Introduction to Outstanding Research (Videos)
張翼副校長 – 新世代半導體─氮化鎵元件之通訊應用
Dean Kung-Hwa Wei – Polymer Nanocomposites for Optoelectronic Applications
陳三元老師 – 對腫瘤具雙重免疫療效功能之奈米褐藻醣藥物
林宏洲老師 – 尖端有機及高分子(軟性)材料
陳智老師 – (111)奈米雙晶銅研發與其在微電子元件的應用
吳樸偉老師 – Large-Area Colloidal Crystals and Inverse Opals for Engineering Applications
林欣杰老師 – 奈米超分子材料
黃爾文老師 – 大數據時代的金屬3D列印
鄒年棣老師 – 3D列印仿生骨釘設計與計算模擬
張仍奎老師 – 儲能材料
吳欣潔老師 – 熱電材料
Introduction to Alumni Studying Abroad
交通大學材料系指考甲組、乙組特色及優勢介紹
Congratulations to the Department for its Advantageous Programs and Improvement in College Entrance Exam Rankings, Featured in the Media!
Collaborating with Prestigious U.S. Universities and TSMC to Promote Advantageous Programs, National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University’s Materials Science Department Sees a Significant Jump in College Entrance Exam Rankings
In the 108th academic year, the Department of Materials Science at National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University introduced Group A, which for the first time secured a spot in the top 12 of the second category in the college entrance exam rankings, with an admission score of 409.2 points, marking a significant jump of 30 spots. Amid the general popularity of computer science-related departments, the remarkable rise of the materials science department has sparked heated discussion. The main reason behind this success is the launch of two highly advantageous programs: the "UIUC 3+2 Dual Degree Program" and the "TSMC Program," which have attracted excellent high school students interested in further studying abroad or pursuing careers in high-tech industries. As a result, Group B of the Department of Materials Science has also seen a significant rise, moving up to 25th place in the second category, with an admission score of 397.0 points, making it one of the most sought-after departments in the second category.
Below are several short clips that briefly introduce the interesting courses you will learn in the Department of Materials Science and how they are applied in various research fields.
陳智老師 – 交通大學材料科學與工程學系簡介
| 陳智老師 – 材料科學與工程簡介 |
| 電子/半導體材料-陳智教授 |
| 陶瓷材料-朱英豪教授 |
| 尖端有機及高分子(軟性)材料-林宏洲教授 |
| 金屬材料-黃爾文教授 |
| 奈米材料領域簡介-徐雍鎣教授 |
| 物理與材料科學-曾院介教授 |
| 材料微結構分析-吳文偉教授 |
| 材料科學與數學計算-鄒年棣教授 |
| 能源材料-王誠佑教授 |
| 儲能材料-張仍奎教授 |
| 熱電材料-吳欣潔教授 |
|
多功能生醫材料在醫療應用-陳三元教授 |
Course Introduction
在交大材料系學生能含跨learning about the structure, properties, and interactions of materials. The field of materials engineering is quite broad. Industries such as information technology, communications, electromechanics, energy, chemical materials, defense, and daily life all rely on the foundation of materials science. Furthermore, the production and manufacturing of any product requires materials. Many bottlenecks in the creation of key components across various fields can only be resolved through the development of new materials or the improvement of material processing. As such, materials engineering professionals are in high demand in the industry, and thus, the materials engineering field is unlikely to become obsolete.
>交大材料課程特色
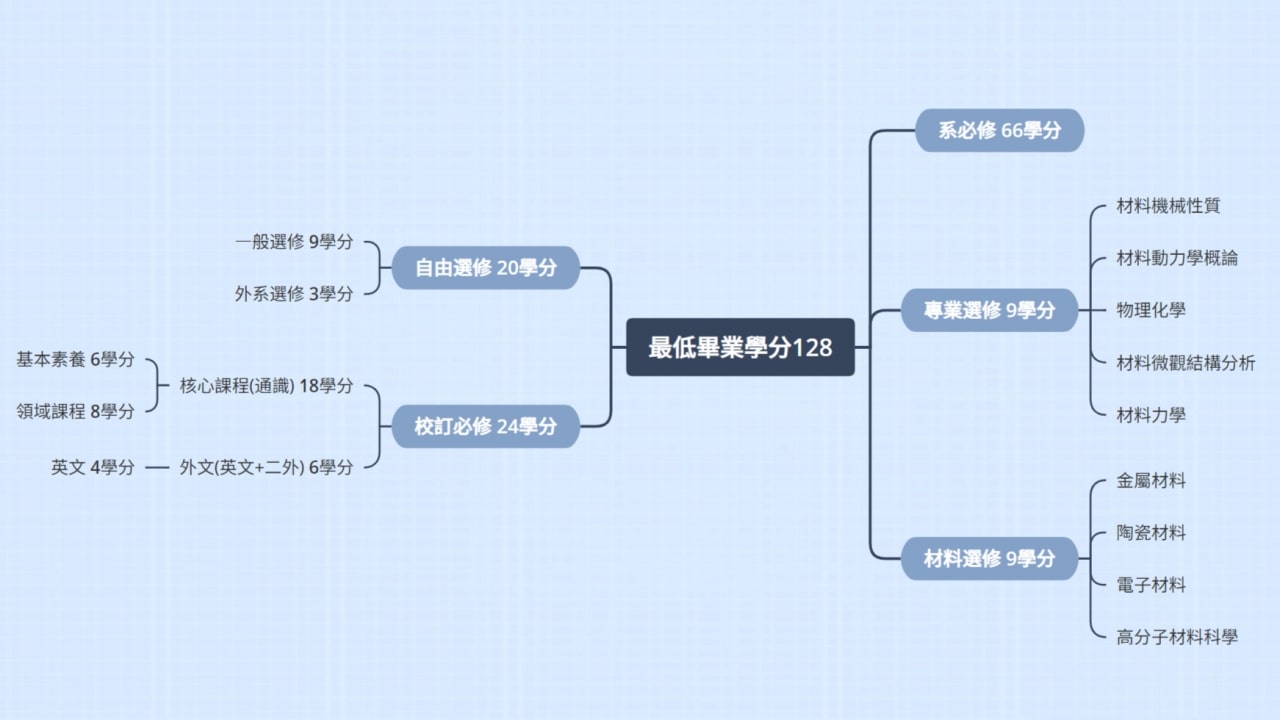
- Flexible Course Options
Only 66 credits are required as mandatory courses by the department, providing students with great freedom in course selection. - 三一學程
材料系、光電系、電物系合作的跨領域學程,設計給尚未確定興趣的學生,可探索工學院、電機學院、理學院的各項課程,從中了解自己的興趣和天賦,並培育材料、光電、電子物理的跨領域人才。共有十項模組課程,讓學生依興趣選擇其中三項(或以上)進行修課。修習三一學程的學生,本系必修只需38學分,跨領域的模組課程,彈性運用時間,加強發展第二專長。1. 電物
電子物理系與材料系的相關合作主要是在半導體方面,電物系擁有的專業量子理論,與材料系的半導體製程相輔相成,可以讓材料系和電物系的學生,了解半導體產業的製程端與理論基礎的關係。2. Optoelectronics
In the study of the properties of light and electricity, the Department of Optoelectronics often requires advanced and superior materials for support. The knowledge learned in the Department of Materials Science can be applied to this field, particularly in the areas of optoelectronic semiconductors and solar panel applications, which are areas where collaboration between the Department of Optoelectronics and the Department of Materials Science is highly beneficial.3. 材料
材料科學與工程學系在三一學程中扮演的角色,是讓學生認識材料結構與性質的關係,以及材料的製造過程;根據不同的研究方向,學生可選擇感興趣的相關課程,並與電物系與光電系的知識相互銜接。
Introduction to the Core Requirements of the Materials Science Department
Introduction to Materials Science and Engineering
- Time: First Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: The theoretical foundations of materials science, covering the basic concepts of materials science and materials engineering. The course content will include atomic structure, material microstructure, mechanical properties, optical and thermal properties, material defects, phase diagrams, strengthening mechanisms, and more. This will lay the groundwork for future studies in materials science, providing essential prerequisite knowledge. The course will also provide an overview of the basic science and applications of ceramic materials, polymer materials, electronic materials, magnetic materials, composite materials, and semiconductors.
- Click here to view OCW
Materials Thermodynamics
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: The first semester focuses on the fundamentals of the three laws of materials thermodynamics. Materials Thermodynamics II will extensively apply the three key thermodynamic concepts learned in Materials Thermodynamics I to unit and multi-phase equilibrium, gas molecular behavior, solution behavior, and more.
- Click here to view OCW
Physical Metallurgy
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: This course covers the basic applications of phase diagrams, diffusion behavior, nucleation and growth, as well as phase transformation behavior. It also discusses various material analysis methods and their applications. Upon completing this course, students will be able to explain fundamental metallurgical phenomena, distinguish the composition and properties of different alloys, and understand the properties of metal structures.
Introduction to Crystal Structures and Diffraction
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 3 credits, only in the second semester
- Course Description: This course primarily covers the following topics: 1. The basic crystallography concepts, including the symmetry, classification, point groups, and space groups of crystal structures, as well as important crystal structures. 2. Introduction to X-ray sources, the construction of reciprocal lattices, the basic principles of X-ray diffraction, and various fundamental applications of X-ray diffraction in materials analysis.
Introduction to Computer Science
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 3 credits, only in the first semester
- Course Description: Programming has become a common skill in the engineering field, and materials science often uses programming to simulate the microscopic structure and properties of materials. This course is therefore a mandatory requirement for the department. In this course, students will have hands-on opportunities to become familiar with Python syntax.
Basic Materials Laboratory
- Time: Second Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: Students will apply the theoretical knowledge learned in class to conduct a series of materials experiments, covering areas such as metallography and electrochemistry.
Materials Engineering Laboratory
- Time: Third Year
- Credits: 6 credits in total, split across both semesters
- Course Description: This is a more advanced laboratory course. In this class, students will learn polymer synthesis, preparation, and characterization, as well as the analysis of the optical and electrical properties of polymers.
>Course Map
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 3+2 Dual Degree Program
National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University’s Department of Materials Science actively collaborates with world-class international universities, encouraging students to go global. The department has launched a 3+2 Dual Degree Program with the Department of Materials Science at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC). This program allows students to earn both a Master's degree in Materials Science from UIUC and a Bachelor's degree in Materials Science from National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University in just five years.

Dual Degree Program Introduction
Features and Advantages
This program is currently the only one of its kind in Taiwan's top universities and is one of the best options for students who wish to pursue a dual degree program with a prestigious U.S. university. The partner university is ranked sixth in the U.S. News Materials Science department, providing a great opportunity for students who wish to further their studies and career in the U.S. Additionally, obtaining a U.S. master's degree typically takes six years (four years of undergraduate studies and two years of graduate studies), but this 3+2 program allows students to earn a master's degree from a top U.S. university one year earlier than the standard timeline. Therefore, this program enables students to graduate a year earlier and start working in the U.S. industry.
This dual degree program significantly **lowers the threshold for NYCU Materials Science students to study abroad at top U.S. universities**. Generally, applying to U.S. research institutions requires taking the TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language) and GRE (Graduate Record Examination). TOEFL scores must exceed the minimum requirement set by each university, and GRE scores must meet specific standards. However, since this program allows students to begin their studies at the University of Illinois starting in their fourth year of university, applicants are not required to submit GRE scores. Additionally, even if the TOEFL score does not meet the threshold, students can still apply and take English courses at the University of Illinois to improve their proficiency. The academic requirement is a GPA of 3.0 or higher, which is achievable for approximately the top 60% of NYCU Materials Science students.
Application Requirements
- Undergraduate Academic Requirements: During the 3 years of study in the Department of Materials Science at NYCU, students must maintain a GPA of no less than 3.0 (on a 4.0 scale). Currently, the average GPA of successful applicants is 3.5 or higher.
- Language Requirements: An average IELTS score of no less than 7.5, or an average TOEFL score of no less than 104.
- GRE Requirements: The GRE is required and can be taken during the first semester of the 3+2 program. The average score requirements are: Quantitative: 86% Verbal: 72% Writing Assessment: 51%
FAQs
A: The tuition and accommodation fees are the same as those for graduate students at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (without the requirement to write a thesis). The average annual tuition for graduate students is USD $34,330, and 36 credit hours must be completed over two years. The total estimated annual cost for tuition, accommodation, and living expenses is approximately USD $57,000 (about NT$1.7 million). For more information, please refer to the following webpage: https://cost.illinois.edu/Home/Cost
Q2: When can I apply, and what documents are required?
- Transcripts
- TOEFL or IELTS scores (within two years)
- Statement of Purpose
- Study Plan (How many credits have been completed so far? What courses will be completed in the second semester of junior year? Which courses will be taken at UIUC?)
Others
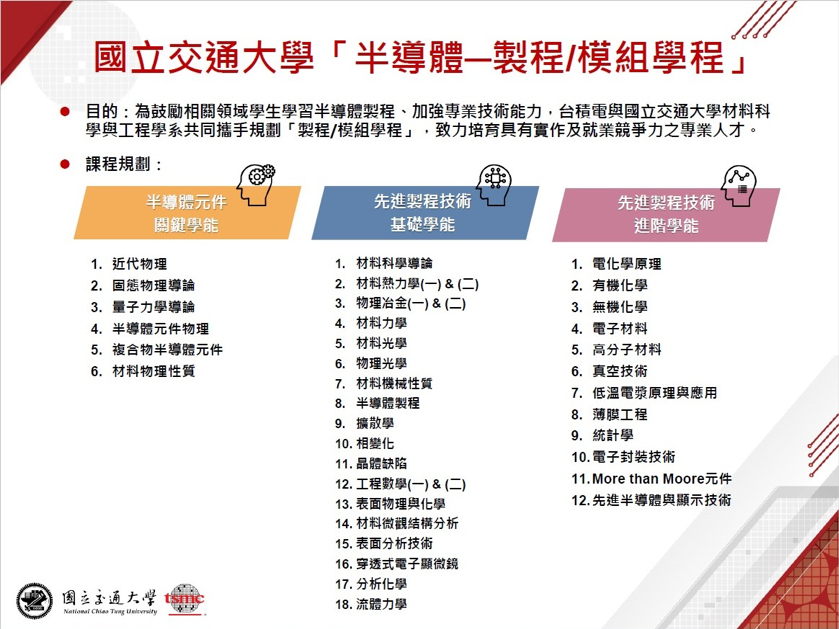
交通大學攜手台積電開設半導體學程
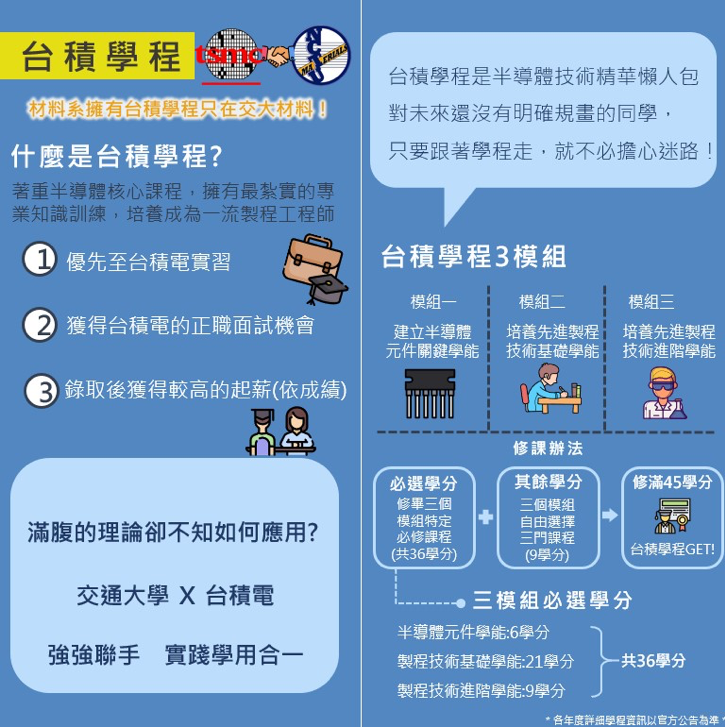
Allowing Students to Ride the Fast Track to Semiconductor Research and Development!
The "Semiconductor - Process/Module" Program, jointly created by the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at NYCU and TSMC, guarantees an interview!
交大攜手台積電 培育半導體人才
Reporter: Pan Tao-Yu, March 30, 2020

TSMC has always been a dream company for many graduates, and the semiconductor program jointly offered by National Chiao Tung University and TSMC undoubtedly provides students with a great internship opportunity, while also guaranteeing an interview after graduation, serving as a "fast track" to the workforce.
This program mainly offers two major tracks: "Semiconductor - Devices/Integration" and "Semiconductor - Process/Module," aimed at cultivating industry professionals with practical process experience and employment competitiveness. Due to its focus on core courses and the achievable credit requirements, the program has attracted many students interested in the semiconductor industry. Students who complete the required courses in the program will receive a completion certificate jointly signed and issued by the department and TSMC. NYCU Acting President, Dr. Chen Hsin-Hong, stated that this collaboration with TSMC creates the best platform for integrating theory and practice, allowing students to gain solid semiconductor expertise and practical training, thus reducing the gap between education and employment. He looks forward to further collaborations with TSMC to drive the development of industry-academia partnerships in Taiwan.
Process/Module Program
The "Process/Module Program" is led by the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, jointly developed with TSMC. The curriculum covers a wide range of courses related to materials, chemistry, physics, electronics, and mechanical engineering. The elective courses are also quite diverse, with highlights including topics such as microstructure and surface analysis, More than Moore devices, and advanced semiconductor and display technologies.
The program was designed by TSMC's Technology Committee Director, Chen Chao-Cheng, who stated, "For example, when encountering process imaging defects in work, it's not just about relying on material knowledge to solve the problem. One also needs to understand the principles of physical and chemical reactions, integrating and applying knowledge from various fields to solve the problem." Therefore, the talent required by the industry is multifaceted. The semiconductor program's curriculum provides an exemplary reference, enabling students to plan their course paths early. At the same time, he hopes for more opportunities for close collaboration and interaction between schools and businesses, continuing to work towards reducing the gap between academic training and industry needs.

Devices/Integration Program
The "Devices/Integration Program" is jointly planned by the Department of Electrical Engineering, the Institute of Electronics, and TSMC. The curriculum covers aspects such as device development, advanced process integration, and materials analysis techniques. In addition to emphasizing practical courses, the program also includes specialized courses such as extreme ultraviolet lithography technology, new memory types, and neuromorphic computing. TSMC's Technology Committee Director, Zhang Ze-En, shared that he himself has a professional background. After earning his Ph.D. at NYCU, he entered the industry and deeply felt the gap between academia and industry. The most noticeable issue he observed was that the rapid pace of technological advancements in high-tech fields often leaves textbooks behind, making it difficult for students to keep up with cutting-edge industry developments. As a result, students graduate with a wealth of theoretical knowledge but lack practical application skills. Moreover, the challenges faced in the workplace are often complex and multifaceted, and single-discipline knowledge is insufficient to tackle them. To address this, he and the professors spent a considerable amount of time discussing and refining the program's design.


Related Reports
Guaranteed Interview! NYCU Partners with TSMC to Cultivate Semiconductor Talent
Industry-Academia Collaboration Made Easy: NYCU Partners with TSMC to Launch Semiconductor Program
Partnering with TSMC to Launch Semiconductor Program with Guaranteed Interview After Graduation
